Optimizing Task Flow Time: A Comprehensive Guide
This article talks about unlocking productivity through strategic task flow optimization.
What is Task flow time?🤔
Task flow time is the time taken to complete a sequence of tasks or activities from initiation to completion. It is the time required for a set of interconnected steps to be carried out, often within a process or workflow. Understanding and optimizing task flow time is crucial for improving efficiency, productivity, and the overall performance of an organization.
Significance of task flow time
The significance of task flow time lies in its pivotal role in shaping organizational efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. The duration it takes to complete a sequence of tasks influences operational costs, resource utilization, and overall project.
Shorter task flow times improve customer satisfaction through timely deliveries and consistent quality and empower organizations to be more agile and responsive in a dynamic market. Effective management of task flow increases employee productivity by reducing workloads and enabling a focus on tasks that add value. Ultimately, organizations that prioritize the optimization of task flow times position themselves for operational excellence, cost-effectiveness, and a competitive edge in their respective industries.
What are the challenges in task flow time?
The challenges associated with task flow time are multifaceted and can significantly affect organizational efficiency. One key challenge exists in identifying bottlenecks within the task flow, where some steps or processes slow the smooth progression of work. These bottlenecks may occur because of limited resources, outdated technologies, or inefficient procedures. Communication gaps pose another challenge, as unclear or delayed communication between team members can lead to disruptions in the task flow. Moreover, the complexity of some tasks and the need between them can contribute to longer task flow times. Inadequate training and skill gaps among team members may also hinder the streamlined execution of tasks. External factors such as market changes or unforeseen events can have an effect. Maintaining consistent and optimal task flow times is a challenge. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive method involving process optimization, technology upgrades, improved communication strategies, and continuous training initiatives to foster a more resilient and efficient task flow.
Assessing Current Workflow
Task Analysis:
Task analysis is a systematic process to reduce a complex task or activity into smaller, manageable components. The primary goal is to gain insights into the specific actions, cognitive processes, and interactions involved in the performance of a task. Across various fields, this method is efficient, including instructional design, human-computer interaction, and business process optimization.
Components of Task Analysis
Task Identification: Begin by clearly defining the task or activity that needs analysis then establish the goals and objectives associated with the task.
Breaking Down the Task: Identify the subtasks or steps involved in accomplishing the overall task then break down each subtask further into specific actions or decisions.
Time Tracking
Time tracking is a crucial practice that involves monitoring and recording the time spent on various activities or tasks. It is widely used across industries, serving multiple purposes, from enhancing personal productivity to optimizing organizational processes. Here's an overview of time tracking, its methods, and its significance:
Methods of Time Tracking:
Manual Methods: Record tasks' start and end times on a timesheet.
Automated Methods: Use specialized tools to automate the process and track time spent on tasks. Integrate time-tracking features in project management platforms.
Components of Time Tracking:
Task or Activity Identification: Clearly define and identify the tasks or activities.
Time Logging: Regularly record the start and end times of tasks, and note any breaks or interruptions during the task.
Categorization: Categorize time entries based on projects, clients, or types of activities. Categorization helps in analyzing how time among different responsibilities is shared.
Review and analysis: Periodically review time logs to assess productivity and identify areas for improvement. Analyze patterns and trends in time allocation.
Identifying Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks slow down the flow of work in a system or process, causing delays and inefficiencies. Identifying and overcoming bottlenecks is crucial for enhancing overall workflow and operational efficiency. A bottleneck may manifest because of various factors, including resource constraints, outdated technologies, communication breakdowns, or inefficient processes. Some ways of addressing bottlenecks are:
- Pinpointing Bottlenecks
Pinpointing bottlenecks in a workflow is a critical step in improving efficiency and streamlining processes. A bottleneck occurs when a point in a system slows down or obstructs the flow of work, often causing delays and inefficiencies. Identifying and addressing bottlenecks is crucial for optimizing workflows and enhancing overall efficiency. Begin by precisely mapping out the entire workflow, breaking it into distinct stages, and documenting dependencies. Use performance metrics to collect data on each stage, identifying areas with prolonged cycle times or frequent delays. Analyze workflow patterns and carry out interviews to gain insights from team members. Evaluate resource allocation and technology effectiveness at each stage, considering whether existing tools contribute to or hinder workflow efficiency. Implement time tracking to measure task durations and prioritize addressing bottlenecks in critical stages that impact the overall timeline. Assess communication channels and promote a collaborative problem-solving approach involving cross-functional teams to brainstorm solutions. Continuous improvement is crucial and requires iterative assessments, adaptability, and the use of changes by trying out a small-scale trial before fully implementing it. Organizations can systematically identify a more streamlined and productive workflow by taking these steps.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process employed to identify the underlying causes of problems or issues within a system or process.
This method is essential for organizations aiming to address issues at their source rather than merely treating symptoms. Conducting an effective RCA is a systematic and strategic process aimed at identifying the fundamental issues underlying problems within a system or process. The first step involves clearly defining the problem and understanding its impact on the overall operations. Gather relevant information by collecting data and consulting with stakeholders. Using tools such as the fishbone diagram and the 5 Why technique, a cross-functional team engages in a thorough examination to know potential causes.
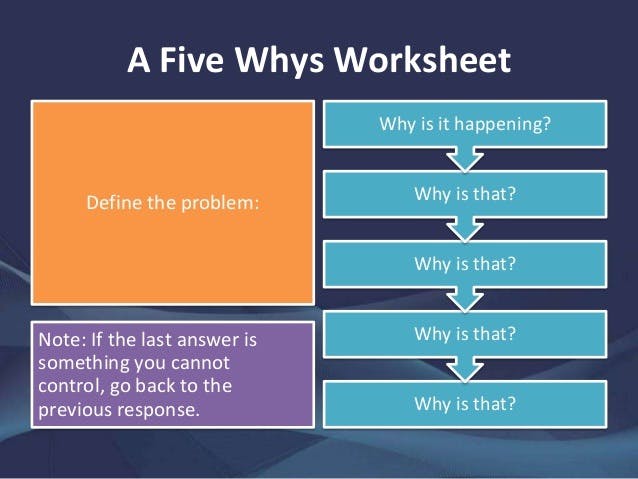
The Pareto analysis helps prioritize these causes, focusing efforts on the most impactful factors. The team identifies root causes and then examines and validates them rigorously, generating corrective actions with careful consideration of associated risks. Continuous monitoring and a closed-loop feedback system follow the implementation of these solutions, creating a culture of ongoing evaluation and improvement. This comprehensive guide ensures organizations can systematically address issues at their source, fostering resilient and lasting solutions that prevent recurrence.
Strategies for Reduction
Reducing task flow time encompasses various approaches to enhance efficiency and productivity. Process optimization involves streamlining workflows by eliminating redundancies and unnecessary steps. Automation of repetitive tasks using suitable technologies contributes significantly to time savings. Improving communication channels within and between teams fosters collaboration and swift information exchange. Resource allocation enables the optimal use of human resources and technology. Training and skill development initiatives empower employees to perform tasks more efficiently. Incremental implementation of changes helps organizations adapt gradually, minimizing disruptions. The assessment of implemented strategies and making necessary adjustments rely heavily on monitoring and evaluation. Real-world examples and success stories illustrate the effectiveness of these strategies in reducing task flow time. Organizations can successfully optimize their task flows, resulting in increased productivity and a competitive edge in the market by adopting a comprehensive and iterative approach organizations can.
Implementing Changes
Implementing changes in task flow management involves a systematic and strategic process to ensure a smooth transition and sustained improvement. The first step is to pilot changes on a smaller scale, allowing for testing and refinement before full-scale integration. During this phase, it is crucial to monitor the impact of the changes and collect feedback from stakeholders and team members. Continuous communication and collaboration are essential to keep all parties informed and engaged throughout the implementation process. A data-driven approach, supported by key performance indicators and metrics, helps measure the effectiveness of the changes. Flexibility is crucial, allowing for adjustments based on real-time feedback and growing organizational needs. As they roll out changes, providing adequate training and support to employees ensures a successful adaptation to new workflows. By fostering a culture of adaptability and continuous improvement, organizations can navigate the challenges associated with change and achieve sustained efficiency gains in their task flow management.
Case studies: Real-world examples
Several organizations have successfully reduced task flow time, demonstrating the positive impact of strategic changes in their workflows. One notable example is Toyota, which pioneered the Lean Production System. Toyota significantly reduced production lead time and increased overall efficiency by implementing principles such as just-in-time manufacturing and continuous improvement. Another example is Amazon, for its commitment to optimizing operational processes. Through advanced logistics, automation, and data-driven decision-making, Amazon has streamlined order fulfillment and delivery processes, decimating task flow times in their massive supply chain. Google has embraced agile development methodologies, allowing faster software development cycles and quicker responses to changing market demands. These organizations showcase that process optimization, technology integration, and a commitment to continuous improvement can substantially reduce task flow time across various industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, successfully reducing task flow time is a transformative journey for organizations, unlocking heightened efficiency and responsiveness. The points from this exploration include the recognition that systematic task analysis, identification of bottlenecks, and the strategic implementation of changes are pivotal in. achieving streamlined workflows. Real-world case studies, from automotive giants to tech innovators, underscore the adaptability and success achievable through tailored strategies such as automation, process optimization, and enhanced communication channels. The call to action for organizations is clear: prioritize continuous improvement, invest in technological advancements, and foster a culture that embraces change. By doing so, organizations can meet the challenges of today's dynamic business landscape and gain a competitive edge by achieving optimal task flow times, ensuring sustained success in the growing marketplace.
